ดินแดนของสหรัฐ
ลิงก์ข้ามภาษาในบทความนี้ มีไว้ให้ผู้อ่านและผู้ร่วมแก้ไขบทความศึกษาเพิ่มเติมโดยสะดวก เนื่องจากวิกิพีเดียภาษาไทยยังไม่มีบทความดังกล่าว กระนั้น ควรรีบสร้างเป็นบทความโดยเร็วที่สุด |
หน้านี้มีเนื้อหาเป็นภาษาต่างประเทศ คุณสามารถช่วยพัฒนาหน้านี้ได้ด้วยการแปล ยกเว้นหากเนื้อหาเกือบทั้งหมดไม่ใช่ภาษาไทย ให้แจ้งลบแทน |
ดินแดนของสหรัฐ | |
|---|---|
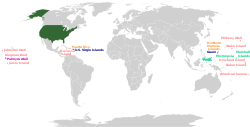 ดินแดนไม่มีการจัดระเบียบซึ่งปกครองโดยระบบเทศบาล
ดินแดนที่มีสถานภาพเครือจักรภพซึ่งไม่ได้ปกครองโดยระบบเทศบาล
ดินแดนไม่มีการจัดระเบียบซึ่งปกครองโดยระบบเทศบาล
ดินแดนไม่มีการจัดระเบียบซึ่งไม่ได้ปกครองโดยระบบเทศบาล | |
| นิคมใหญ่สุด | ซานฆวน, ปวยร์โตรีโก |
| ภาษา | อังกฤษ, สเปน, ชามอร์โร, คาโรไลน์, ซามัว |
| เดมะนิม | ชาวอเมริกัน |
| ดินแดน | 5 ดินแดนที่มีประชากร 9 ดินแดนที่ไม่มีประชากรถาวร 2 ดินแดนที่ยังอยู่ในข้อพิพาท |
| ผู้นำ | |
| โจ ไบเดิน | |
| ดูรายชื่อผู้ว่าการดินแดนในปัจจุบัน | |
| พื้นที่ | |
• รวม | 22,294.19 ตารางกิโลเมตร (8,607.83 ตารางไมล์) |
| ประชากร | |
• ประมาณ | 4,100,954 คน ใน ค.ศ. 2010[1] 3,569,284 คน ใน ค.ศ. 2020[2][3][4][5][6][7][note 1] |
| สกุลเงิน | ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ |
| รูปแบบวันที่ | ดด/วว/ปปปป (AD) |
| |
การแบ่งประเภทดินแดนสหรัฐอเมริกาปัจจุบัน
แก้ สหรัฐอเมริกา
ดินแดนไม่มีการจัดระเบียบซึ่งปกครองโดยระบบเทศบาล
ดินแดนมีการจัดระเบียบซึ่งไม่ได้ปกครองโดยระบบเทศบาล
สถานภาพเครือจักรภพ
ดินแดนไม่มีการจัดระเบียบซึ่งไม่ได้ปกครองโดยระบบเทศบาล
ดินแดนมีการจัดระเบียบซึ่งปกครองโดยระบบเทศบาล
แก้ดินแดนไม่มีการจัดระเบียบซึ่งไม่ได้ปกครองโดยระบบเทศบาล
แก้ดินแดนมีการจัดระเบียบซึ่งไม่ได้ปกครองโดยระบบเทศบาล
แก้| ชื่อ | ตำแหน่ง | พื้นที่ | จำนวนประชากร | เมืองหลวง | ข้อมูล |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| กวม | ไมโครนีเซีย & แปซิฟิกเหนือ | 543 km2 (210 sq mi) | 159,358 | ฮากัตญา | Territory since 1898, Guam is the home of Naval Base Guam and Andersen Air Force Base. |
| หมู่เกาะนอร์เทิร์นมาเรียนา | ไมโครนีเซีย & แปซิฟิกเหนือ | 463.63 km2 (179 sq mi) | 77,000 | ไซปัน | Commonwealth since 1978; formerly a United Nations Trust Territory under the administration of the U.S. |
| ปวยร์โตรีโก | แคริบเบียน & แอตแลนติกเหนือ | 9,104 km2 (3,515 sq mi) | 3,667,084 | ซานฮวน | Territory since 1898, a commonwealth since 1952. In November 2008 a district court judge ruled that a sequence of Congressional actions have had the cumulative effect of changing Puerto Rico's status to incorporated.[11] However, by April 2011 the issue had not yet made its way through the courts,[12] and in January 2013 the U.S. government still referred to Puerto Rico as unincorporated.[13] |
| หมู่เกาะเวอร์จินของสหรัฐ | แคริบเบียน & แอตแลนติกเหนือ | 346.36 km2 (134 sq mi) | 106,405 | ชาร์ลอตต์อะมาลี | สหรัฐอเมริกาซื้อจากเดนมาร์กในปี 1917 |
ดินแดนไม่มีการจัดระเบียบซึ่งปกครองโดยระบบเทศบาล
แก้| ชื่อ | ตำแหน่ง | พื้นที่ | จำนวนประชากร | เมืองหลวง | ข้อมูล |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| อเมริกันซามัว | พอลินีเซีย & แปซิฟิกใต้ | 197.1 km2 (76 sq mi) | 55,519 | ปาโกปาโก | Territory since 1898. Locally self-governing under a constitution last revised in 1967.[15] |
| เกาะเบเกอร์[a] | แปซิฟิกเหนือ | 2.1 km2 (1 sq mi) | 0 | ||
| เกาะฮาวแลนด์[a] | แปซิฟิกเหนือ | 1,112.0 เอเคอร์ (450 เฮกตาร์) | 0 | Claimed under the Guano Islands Act in 1856 | |
| เกาะจาร์วิส[a] | พอลินีเซีย & แปซิฟิกใต้ | 4.5 km2 (2 sq mi) | 0 | Claimed under the Guano Islands Act in 1857, formally annexed on February 27, 1858 | |
| จอห์นสตันอะทอลล์[a] | แปซิฟิกเหนือ | 4.5 km2 (2 sq mi) | 0 | last used by the Department of Defense in about 2005 | |
| คิงแมนรีฟ[a] | พอลินีเซีย & แปซิฟิกเหนือ | 18 km2 (7 sq mi) | 0 | Claimed under the Guano Islands Act in 1860, formally annexed in 1922 | |
| เกาะเวก[a] | ไมโครนีเซีย & แปซิฟิกเหนือ | 7.4 km2 (3 sq mi) | 150 | Territory since 1898; primarily a wildlife refuge; host to the Wake Island Airfield administered by U.S. Air Force; claimed by the Marshall Islands.[16] | |
| เกาะมิดเวย์ | แปซิฟิกเหนือ | 6.2 km2 (2 sq mi) | 0 | Territory since 1859; primarily a wildlife refuge inhabited only by civilian contractors; previously under the jurisdiction of the Department of the Navy. | |
| เกาะนาแวสซา | แคริบเบียน & แปซิฟิกเหนือ | 5.4 km2 (2 sq mi) | 0 | Territory since 1857. Claimed by Haiti. | |
| เซร์รานียาแบงก์ | แคริบเบียน & แอตแลนติกเหนือ | 350 km2 (135 sq mi) | 0 | Administered by Colombia; site of a naval garrison. Claimed by the United States (since 1879 under the Guano Islands Act) and Honduras. A claim by Nicaragua was resolved in 2012 in favor of Colombia by the International Court of Justice.[17] | |
| บาโฮนวยโวแบงก์ | แคริบเบียน & แอตแลนติกเหนือ | 110 km2 (42 sq mi) | 0 | Administered by Colombia. Claimed by the United States (under the Guano Islands Act), Jamaica, and Nicaragua |
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 These six territories, together with Palmyra Atoll, comprise the Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument.
การแบ่งประเภทอดีตดินแดนและอาณาเขตในปกครองของสหรัฐอเมริกา
แก้อดีตดินแดนมีการจัดระเบียบซึ่งไม่ได้ปกครองโดยระบบเทศบาลของสหรัฐอเมริกา
แก้ดู Organized incorporated territories of the United States for a complete list.
อดีตดินแดนไม่มีการจัดระเบียบของสหรัฐอเมริกา
แก้- Corn Islands (1914–1971)
- หมู่เกาะไลน์ (? – 1979)
- เขตคลองปานามา (1903–1979)
- หมู่เกาะฟิลิปปินส์ (1898–1935), เครือรัฐฟิลิปปินส์ (1935–46)
- Phoenix Islands (?–1979)
- Quita Sueño Bank (1869–1981)
- Roncador Bank (1856–1981)
- เซร์รานียาแบงก์ (?–1981)
- Swan Islands (1863–1972)
อดีตดินแดนไม่มีการจัดระเบียบของสหรัฐอเมริกาซึ่งปกครองโดยรัฐบาลทหาร
แก้- ปวยร์โตรีโก (April 11, 1899 – May 1, 1900): civil government operations began
- ฟิลิปปินส์ (August 14, 1898[18] – July 4, 1901): civil government operations began
- กวม (April 11, 1899 – July 1, 1950): civil government operations began
พื้นที่ซึ่งเดิมสหรัฐอเมริกาปกครอง
แก้- คิวบา (April 11, 1899 – May 20, 1902)
- ฟิลิปปินส์ (August 14, 1898 – July 4, 1946)
- เบรากรุซ was occupied Vera Cruz on the coast of Mexico by the United States for six months, from April 21, 1914 to November 23, 1914, consequential to the Tampico Affair following the Mexican Revolution of 1910-1929.
- เฮติ on the western third of the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea was occupied by the United States from 1915 to 1934. Also later occupied along with the authority of the United Nations during 1999 to 2000's.
- สาธารณรัฐโดมินิกัน on the eastern two-thirds of the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea was occupied by the United States from 1916 to 1924 and again from 1965 to 1966.
- ดินแดนในภาวะทรัสตีหมู่เกาะแปซิฟิก (1947–1986)
- หมู่เกาะรีวกีว อยู่ในทะเลจีนตะวันออก รวมโอะกินะวะ (สหรัฐอเมริกายึดครอง: 1952–1972, หลัง สงครามโลกครั้งที่สอง)
- Nanpo Islands (1945–1968)
- Marcus Island (หรือ Minamitorishima) (1945–1968)
- หมู่เกาะฟอล์กแลนด์ (1831–1832)
เขตอื่น ๆ
แก้- การยึดครองกรีนแลนด์ของสหรัฐอเมริกา (1941–1945)[19]
- การยึดครองไอซ์แลนด์ของสหรัฐอเมริกา (1941–1946)[19]
- เขตยึดครองของสหรัฐอเมริกาในออสเตรียที่ฝ่ายสัมพันธมิตรยึดครอง และ เวียนนา (1945–1955)
- เขตยึดครองของสหรัฐอเมริกาในเบอร์ลินตะวันตก (1945–1990)
- เขตยึดครองของสหรัฐอเมริกาของเขตยึดครองฝ่ายสัมพันธมิตรในเยอรมนี (1945–1949)
- รัฐบาลทหารฝ่ายสัมพันธมิตรสำหรับดินแดนที่ถูกยึดครอง
- ดินแดนตรีเยสเตเสรี (1947–1954)
- การยึดครองญี่ปุ่น (1945–1952) หลังสงครามโลกครั้งที่สอง
- สหรัฐอเมริกามีส่วนร่วมในการยึดครองไรน์แลนด์ (เยอรมนี) (1918–1921)
- เกาหลีใต้ (U.S. occupation of the south of the 38th parallel north in Korea in 1945–1948). The region is slightly different from the current practical boundary of the Republic of Korea (South Korea) since the ceasefire of the Korean War. See also Division of Korea.
- Coalition Provisional Authority อิรัก (2003–2004)
- Green zone อิรัก (March 20, 2003 – December 31, 2008)[20]
- เกาะกลีแปร์ตอน (1944–1945), ยึดครองดินแดน; ยกให้ฝรั่งเศสในวันที่ 23 ตุลาคม 1945
- เกรเนดา รุกรานและยึดครอง (1983)
ดูเพิ่ม
แก้อ้างอิง
แก้- ↑ อ้างอิงผิดพลาด: ป้ายระบุ
<ref>ไม่ถูกต้อง ไม่มีการกำหนดข้อความสำหรับอ้างอิงชื่อCensus2010_2012 - ↑ อ้างอิงผิดพลาด: ป้ายระบุ
<ref>ไม่ถูกต้อง ไม่มีการกำหนดข้อความสำหรับอ้างอิงชื่อCIAAS - ↑ อ้างอิงผิดพลาด: ป้ายระบุ
<ref>ไม่ถูกต้อง ไม่มีการกำหนดข้อความสำหรับอ้างอิงชื่อCIAGuam - ↑ อ้างอิงผิดพลาด: ป้ายระบุ
<ref>ไม่ถูกต้อง ไม่มีการกำหนดข้อความสำหรับอ้างอิงชื่อCIACNMI - ↑ อ้างอิงผิดพลาด: ป้ายระบุ
<ref>ไม่ถูกต้อง ไม่มีการกำหนดข้อความสำหรับอ้างอิงชื่อCIAPR - ↑ อ้างอิงผิดพลาด: ป้ายระบุ
<ref>ไม่ถูกต้อง ไม่มีการกำหนดข้อความสำหรับอ้างอิงชื่อCIAVI - ↑ https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/PR/ U.S. Census Bureau. QuickFacts - Puerto Rico. Retrieved July 26, 2020.
- ↑ "Definition of Terms—1120 Acquisition of U.S. Nationality in U.S. Territories and Possessions". U.S. Department of State Foreign Affairs Manual Volume 7—Consular Affairs. U.S. Department of State. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิม (PDF)เมื่อ December 22, 2015. สืบค้นเมื่อ January 10, 2016.
- ↑ "AUSTRALIA-OCEANIA :: UNITED STATES PACIFIC ISLAND WILDLIFE REFUGES (TERRITORIES OF THE US)". The World Factbook. US Central Intelligence Agency. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 2019-02-16. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2014-06-27.
- ↑ "Department of the Interior Office of Insular Affairs". เก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 2007-10-31. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2007-10-31.
- ↑ Consejo de Salud Playa Ponce v. Johnny Rullan, p.28: "The Congressional incorporation of Puerto Rico throughout the past century has extended the entire Constitution to the island ...."
- ↑ Hon. Gustavo A. Gelpi, "The Insular Cases: A Comparative Historical Study of Puerto Rico, Hawai'i, and the Philippines", The Federal Lawyer, March/April 2011. http://www.aspira.org/files/legal_opinion_on_pr_insular_cases.pdf เก็บถาวร 2011-04-27 ที่ เวย์แบ็กแมชชีน p. 25: "In light of the [Supreme Court] ruling in Boumediene, in the future the Supreme Court will be called upon to reexamine the Insular Cases doctrine as applied to Puerto Rico and other US territories."
- ↑ accessed 26 January 2013 เก็บถาวร 2013-06-10 ที่ เวย์แบ็กแมชชีน: "Puerto Rico is a self-governing, unincorporated territory of the United States located in the Caribbean".
- ↑ IBP USA (2009), SAMOA American Country Study Guide: Strategic Information and Developments, Int'l Business Publications, pp. 49–64, ISBN 978-1-4387-4187-1, สืบค้นเมื่อ 2011-10-20[ลิงก์เสีย]
- ↑ The revised constitution was approved on June 2, 1967 by Stewart L. Udall, then U.S. Secretary of the Interior, under authority granted on June 29, 1951. It became effective on July 1, 1967.[14]
- ↑ Wake Island entry at The World Factbook
- ↑ International Court of Justice (2012). "Territorial and maritime dispute (Nicaragua vs Colombia)" (PDF). สืบค้นเมื่อ 2013-06-29.
- ↑ Zaide, Sonia M. (1994), The Philippines: A Unique Nation, All-Nations Publishing Co., p. 279, ISBN 971-642-071-4, สืบค้นเมื่อ 2011-10-20
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 In Danger Undaunted: The Anti-Interventionist Movement of 1940–1941 by Justus D. Doenecke:
- ↑ Campbell Robertson; Stephen Farrell (December 31, 2008), Green Zone, Heart of U.S. Occupation, Reverts to Iraqi Control, The New York Times
อ้างอิงผิดพลาด: มีป้ายระบุ <ref> สำหรับกลุ่มชื่อ "note" แต่ไม่พบป้ายระบุ <references group="note"/> ที่สอดคล้องกัน
