รายชื่อกรดอะมิโนมาตรฐาน
รายชื่อกรดอะมิโนมาตรฐาน (List of standard amino acids)
- แสดงโดยสูตรโครงสร้าง (Structures)
สูตรโครงสร้างและสัญลักษณ์และรหัสพันธุกรรม (genetic code) ของ กรดอะมิโน 20 ตัวเป็นดังนี้
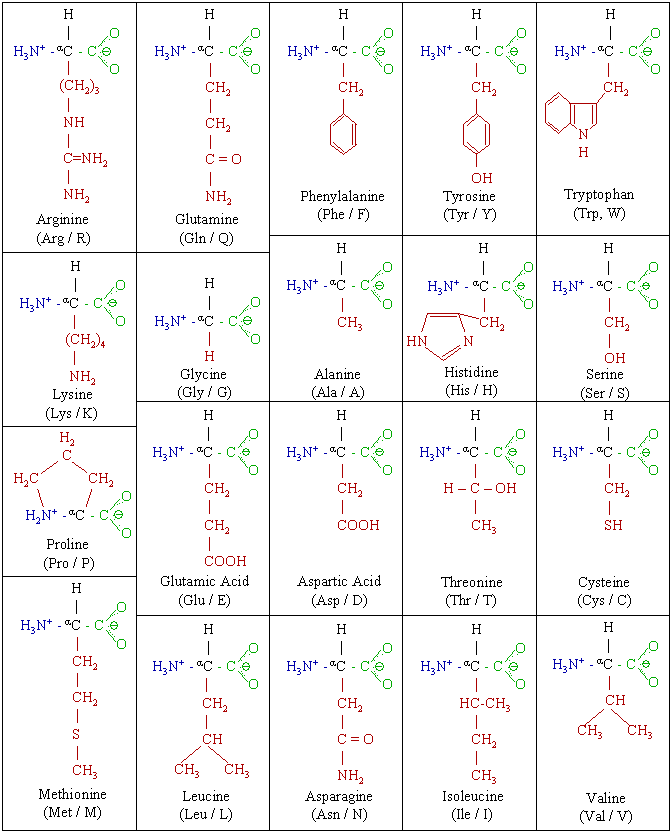
- แสดงรายชื่อกรดอะมิโนและคุณสมบัติทางเคมี (Chemical properties)
แสดงเป็นตารางที่มีทั้งสัญลักษณ์ 1 ตัวอักษร และ 3 ตัวอักษร และคุณสมบัติทางเคมี ซึ่งแตกต่างกันไปตาม โซ่ข้าง (side chains) น้ำหนักโมเลกุล ซึ่งเป็นค่าเฉลี่ยของไอโซโทปทั้งหมดรวมทั้งน้ำหนักของน้ำด้วย (H2O)
| Abbrev. | ชื่อเต็ม (Full Name) | ประเภทโซ่ข้าง (Side chain type) | มวล (Mass) | pI (Isoelectric point) | pK1 (?-COOH) |
pK2 (?-+NH3) |
pKr (R) | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Ala | อะลานีน (Alanine) | ไฮโดรโฟบิก (hydrophobic) | 89.09 | 6.01 | 2.35 | 9.87 | มีจำนวนมากมาย, มีประโยชน์หลายอย่าง มีความแข็งมากกว่าไกลซีน, แต่มีขนาดเล็กพอที่จะจัดวางในตำแหน่งที่เหมาะสมสำหรับโครงสร้างของโปรตีน มันค่อนข้างวางตัวเป็นกลางสามารถอยู่ได้ทั้งเขตที่เป็น ไฮโดรฟิลิก บนโปรตีนส่วนนอก และบริเวณที่เป็นไฮโดรโฟบิกภายใน | |
| C | Cys | ซิสเทอีน (Cysteine) | ไฮโดรโฟบิก (Nagano, 1999) | 121.16 | 5.05 | 1.92 | 10.70 | 8.37 | อะตอมของกำมะถันเชื่อมต่อกับไอออนของ โลหะหนัก ภายใต้ภาวะออกซิไดซิ่ง ซีสตีอิน 2 โมเลกุลสามารถเชื่อมต่อซึ่งกันและกันได้โดน พันธะไดซัลไฟด์ (disulfide bond) และเกิดเป็นกรดอะมิโน ซีสตีน เมื่อซีสตีนเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของโปรตีน อินสุลิน มันจะมีแรงที่ทำให้โครงสร้างของ อินสุลิน เป็นแบบ เทอร์เทียรี่ สตรักเจอร์ และทำให้โปรตีนทนต่อการพับงอและ ผิดธรรมชาติ; การเชื่อมต่อแบบไดซัลไฟด์ (disulphide bridges) พบได้เป็นสิ่งธรรมดาในโปรตีนซึ่งจะต้องทำหน้าที่ในสิ่งแวดล้อมที่รุนแรง, เอนไซม์ย่อยอาหาร (เช่น, เปปซิน และ ไคโมทริปซิน), โปรตีนโครงสร้าง (structural proteins) (เช่น, เคอราติน), และ โปรตีนที่เล็กเกินไปที่จะคงรูปของมันไว้ (เช่น อินสุลิน) |
| D | Asp | กรดแอสปาร์ติก (Aspartic acid) | เป็นกรด | 133.10 | 2.85 | 1.99 | 9.90 | 3.90 | จะทำงานคล้ายกับกรดกลูตามิก เป็นกลุ่มที่เป็นกรดไฮโดรฟิลิกมีประจุลบที่แข็งแกร่ง มักจะตั้งอยู่บนพื้นผิวด้านนอกของโปรตีนทำให้ละลายน้ำได้ จับกับประจุบวกของโมเลกุลและไอออน มักอยู่ร่วมกับเอนไซม์ในการจับกับไอออนโลหะ เมื่ออยู่ด้านในของโปรตีน, aspartate และ glutamate จะมีการจับคู่กับอาร์จินีและไลซีน |
| E | Glu | กรดกลูตามิก (Glutamic acid) | เป็นกรด | 147.13 | 3.15 | 2.10 | 9.47 | 4.07 | จะทำงานคล้ายกับกรด aspartic มีพันธะยาวกว่าและบางกว่า มีความยืดหยุ่นมากกว่า |
| F | Phe | ฟีนิลอะลานีน (Phenylalanine) | ไฮโดรโฟบิก | 165.19 | 5.49 | 2.20 | 9.31 | Essential for humans. Phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan contain large rigid aromatic group on the side chain. These are the biggest amino acids. Like isoleucine, leucine and valine, these are hydrophobic and tend to orient towards the interior of the folded protein molecule. | |
| G | Gly | ไกลซีน (Glycine) | ไฮโดรฟิลิก | 75.07 | 6.06 | 2.35 | 9.78 | Because of the two hydrogen atoms at the ? carbon, glycine is not optically active. It is the tiniest amino acid, rotates easily, adds flexibility to the protein chain. It is able to fit into the tightest spaces, e.g., the triple helix of collagen. As too much flexibility is usually not desired, as a structural component it is less common than alanine. | |
| H | His | ฮีสติดีน (Histidine) | เป็นเบส | 155.16 | 7.60 | 1.80 | 9.33 | 6.04 | In even slightly acidic conditions protonation of the nitrogen occurs, changing the properties of histidine and the polypeptide as a whole. It is used by many proteins as a regulatory mechanism, changing the conformation and behavior of the polypeptide in acidic regions such as the late endosome or lysosome, enforcing conformation change in enzymes. However only a few histidines are needed for this, so it is comparatively scarce. |
| I | Ile | ไอโซลูซีน (Isoleucine) | ไฮโดรโฟบิก | 131.17 | 6.05 | 2.32 | 9.76 | Essential for humans. Isoleucine, leucine and valine have large aliphatic hydrophobic side chains. Their molecules are rigid, and their mutual hydrophobic interactions are important for the correct folding of proteins, as these chains tend to be located inside of the protein molecule. | |
| K | Lys | ไลซีน (Lysine) | เป็นเบส | 146.19 | 9.60 | 2.16 | 9.06 | 10.54 | Essential for humans. Behaves similarly to arginine. Contains a long flexible side-chain with a positively-charged end. The flexibility of the chain makes lysine and arginine suitable for binding to molecules with many negative charges on their surfaces. E.g., DNA-binding proteins have their active regions rich with arginine and lysine. The strong charge makes these two amino acids prone to be located on the outer hydrophilic surfaces of the proteins; when they are found inside, they are usually paired with a corresponding negatively-charged amino acid, e.g., aspartate or glutamate. |
| L | Leu | ลิวซีน (Leucine) | ไฮโดรโฟบิก | 131.17 | 6.01 | 2.33 | 9.74 | Essential for humans. Behaves similar to isoleucine and valine. See isoleucine. | |
| M | Met | เมไทโอนีน (Methionine) | ไฮโดรโฟบิก | 149.21 | 5.74 | 2.13 | 9.28 | Essential for humans. Always the first amino acid to be incorporated into a protein; sometimes removed after translation. Like cysteine, contains sulfur, but with a methyl group instead of hydrogen. This methyl group can be activated, and is used in many reactions where a new carbon atom is being added to another molecule. | |
| N | Asn | แอสพาราจีน (Asparagine) | ไฮโดรฟิลิก | 132.12 | 5.41 | 2.14 | 8.72 | Neutralized version of aspartic acid. | |
| P | Pro | โปรลีน (Proline) | ไฮโดรโฟบิก | 115.13 | 6.30 | 1.95 | 10.64 | Contains an unusual ring to the N-end amine group, which forces the CO-NH amide sequence into a fixed conformation. Can disrupt protein folding structures like ? helix or ? sheet, forcing the desired kink in the protein chain. Common in collagen, where it undergoes a posttranslational modification to hydroxyproline. Uncommon elsewhere. | |
| Q | Gln | กลูตามีน (Glutamine) | ไฮโดรฟิลิก | 146.15 | 5.65 | 2.17 | 9.13 | Neutralized version of glutamic acid. Used in proteins and as a storage for ammonia. | |
| R | Arg | Arginine | เป็นเบส | 174.20 | 10.76 | 1.82 | 8.99 | 12.48 | Functionally similar to lysine. |
| S | Ser | เซอรีน (Serine) | ไฮโดรโฟบิก | 105.09 | 5.68 | 2.19 | 9.21 | Serine and threonine have a short group ended with a hydroxyl group. Its hydrogen is easy to remove, so serine and threonine often act as hydrogen donors in enzymes. Both are very hydrophylic, therefore the outer regions of soluble proteins tend to be rich with them. | |
| T | Thr | ทรีโอนีน (Threonine) | ไฮโดรฟิลิก | 119.12 | 5.60 | 2.09 | 9.10 | Essential for humans. Behaves similarly to serine. | |
| V | Val | วารีน (Valine) | ไฮโดรโฟบิก | 117.15 | 6.00 | 2.39 | 9.74 | Essential for humans. Behaves similarly to isoleucine and leucine. See isoleucine. | |
| W | Trp | ทริปโตแฟน (Tryptophan) | ไฮโดรโฟบิก | 204.23 | 5.89 | 2.46 | 9.41 | Essential for humans. Behaves similarly to phenylalanine and tyrosine (see phenylalanine). Precursor of serotonin. | |
| Y | Tyr | ไทโรซีน (Tyrosine) | ไฮโดรโฟบิก | 181.19 | 5.64 | 2.20 | 9.21 | 10.46 | Behaves similarly to phenylalanine and tryptophan (see phenylalanine). Precursor of melanin, epinephrine, and thyroid hormones. |
| Amino acid | Abbrev. | Side chain | Hydro- phobic | Polar | Charged | Small | Tiny | Aromatic or Aliphatic | van der Waals volume | Codon | Occurrence in proteins (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alanine | Ala, A | -CH3 | X | - | - | X | X | - | 67 | GCU, GCC, GCA, GCG | 7.8 |
| Cysteine | Cys, C | -CH2SH | X | - | - | X | - | - | 86 | UGU, UGC | 1.9 |
| Aspartate | Asp, D | -CH2COOH | - | X | negative | X | - | - | 91 | GAU, GAC | 5.3 |
| Glutamate | Glu, E | -CH2CH2COOH | - | X | negative | - | - | - | 109 | GAA, GAG | 6.3 |
| Phenylalanine | Phe, F | -CH2C6H5 | X | - | - | - | - | Aromatic | 135 | UUU, UUC | 3.9 |
| Glycine | Gly, G | -H | X | - | - | X | X | - | 48 | GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG | 7.2 |
| Histidine | His, H | -CH2-C3H3N2 | - | X | positive | - | - | Aromatic | 118 | CAU, CAC | 2.3 |
| Isoleucine | Ile, I | -CH(CH3)CH2CH3 | X | - | - | - | - | Aliphatic | 124 | AUU, AUC, AUA | 5.3 |
| Lysine | Lys, K | -(CH2)4NH2 | - | X | positive | - | - | - | 135 | AAA, AAG | 5.9 |
| Leucine | Leu, L | -CH2CH(CH3)2 | X | - | - | - | - | Aliphatic | 124 | UUA, UUG, CUU, CUC, CUA, CUG | 9.1 |
| Methionine | Met, M | -CH2CH2SCH3 | X | - | - | - | - | - | 124 | AUG | 2.3 |
| Asparagine | Asn, N | -CH2CONH2 | - | X | - | X | - | - | 96 | AAU, AAC | 4.3 |
| Proline | Pro, P | -CH2CH2CH2- | X | - | - | X | - | - | 90 | CCU, CCC, CCA, CCG | 5.2 |
| Glutamine | Gln, Q | -CH2CH2CONH2 | - | X | - | - | - | - | 114 | CAA, CAG | 4.2 |
| Arginine | Arg, R | -(CH2)3NH-C(NH)NH2 | - | X | positive | - | - | - | 148 | CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, AGG | 5.1 |
| Serine | Ser, S | -CH2OH | - | X | - | X | X | - | 73 | UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU,AGC | 6.8 |
| Threonine | Thr, T | -CH(OH)CH3 | X | X | - | X | - | - | 93 | ACU, ACC, ACA, ACG | 5.9 |
| Valine | Val, V | -CH(CH3)2 | X | - | - | X | - | Aliphatic | 105 | GUU, GUC, GUA, GUG | 6.6 |
| Tryptophan | Trp, W | -CH2C8H5N | X | - | - | - | - | Aromatic | 163 | UGG | 1.4 |
| Tyrosine | Tyr, Y | -CH2-C6H4OH | X | X | - | - | - | Aromatic | 141 | UAU, UAC | 3.2 |