ลิตร
ลิตร (อังกฤษ: litre [บริติช], liter [อเมริกัน]; สัญลักษณ์เอสไอ คือ L และ l[1] สัญลักษณ์อื่น: ℓ) เป็นหน่วยเมตริกของปริมาตร ซึ่งมีค่าเท่ากับ 1 ลูกบาศก์เดซิเมตร (dm3), 1000 ลูกบาศก์เซนติเมตร (ซม.3) หรือ 0.001 ลูกบาศก์เมตร (ม.3) ลูกบาศก์เดซิเมตร (หรือลิตร) มีปริมาตร 10 ซม. × 10 ซม. × 10 ซม. (ดูภาพ) จึงมีค่าเท่ากับหนึ่งในพันลูกบาศก์เมตร
| ลิตร | |
|---|---|
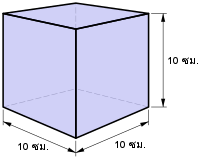 หนึ่งลิตรเท่ากับมวลลูกบาศก์ขนาด 10 เซนติเมตรทุกด้าน | |
| ข้อมูลทั่วไป | |
| ระบบการวัด | หน่วยที่ยอมรับให้ใช้แก่ระบบเอสไอ |
| เป็นหน่วยของ | ปริมาตร |
| สัญลักษณ์ | L หรือ l หรือ (ℓ)[1] |
| ตั้งชื่อตาม | litron |
| การแปลงหน่วย | |
| 1 L ใน ... | ... มีค่าเท่ากับ ... |
| หน่วยฐานเอสไอ | 10−3 m3 |
| ธรรมเนียมสหรัฐ | ≈ 0.264 gallon |

ระบบเมตริกฝรั่งเศสดั้งเดิมใช้ลิตรเป็นหน่วยฐาน คำว่า litre มาจากหน่วยฝรั่งเศสเก่าที่มีชื่อว่า litron ซึ่งมาจากกรีกไบแซนไทน์—โดยเป็นหน่วยน้ำหนัก ไม่ใช่ปริมาตร[2] และมีค่าประมาณ 0.831 ลิตร หน่วยลิตรยังใช้ในระบบเมตริกหลายรูปแบบ และยอมรับใช้ในหน่วยฐานเอสไอ[3] ถึงแม้ว่าจะไม่ใช่หน่วยฐานเอสไอก็ตาม (หน่วยเอสไอของมวลคือลูกบาศก์เมตร (ม.3) สำนักงานชั่งตวงวัดระหว่างประเทศใช้วิธีการสะกดเป็น "litre"[3] ซึ่งเป็นคำที่ใช้ในประเทศที่พูดภาษาอังกฤษ ส่วนรูปสะกด "liter" มักใช้ในภาษาอังกฤษแบบอเมริกัน[a]
น้ำเหลวหนึ่งลิตรมีมวลเกือบเท่ากับหนึ่งกิโลกรัม เพราะเดิมมีการนิยามใน ค.ศ. 1795 ว่า กิโลกรัมเป็นมวลน้ำหนึ่งลูกบาศก์เดซิเมตร ณ อุณหภูมิที่น้ำแข็งละลาย (0 °C)[4] การนิยามเมตรและกิโลกรัมใหม่ในภายหลังทำให้ความสัมพันธ์นี้ถูกยกเลิกไป[5]
หมายเหตุ
แก้- ↑ The Metric Conversion Act of 1985 gives the United States Secretary of Commerce the responsibility of interpreting or modifying the SI for use in the United States. The Secretary of Commerce delegated this authority to the Director of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) (Turner, 2008). In 2008, the NIST published the U.S. version (Taylor and Thompson, 2008a) of the English text of the eighth edition of the Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (BIPM) publication Le Système International d' Unités (SI) (BIPM, 2006). In the NIST publication, the spellings "meter", "liter" and "deka" are used rather than "metre", "litre" and "deca" as in the original BIPM English text (Taylor and Thompson, 2008a, p. iii). The Director of the NIST officially recognized this publication, together with Taylor and Thompson (2008b), as the "legal interpretation" of the SI for the United States (Turner, 2008).
อ้างอิง
แก้- ↑ 1.0 1.1 International Bureau of Weights and Measures (2006), The International System of Units (SI) (PDF) (8th ed.), p. 124, ISBN 92-822-2213-6.
- ↑ Collins English Dictionary.[ต้องการอ้างอิงเต็มรูปแบบ]
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Bureau International des Poids et Mesures, 2006, p. 124. ("Days" and "hours" are examples of other non-SI units that SI accepts.)
- ↑ "Décret relatif aux poids et aux mesures du 18 germinal an 3 (7 avril 1795)" [Weights and measures decree dated 18 Germinal, Year 3 (7 April 1795)] (ภาษาฝรั่งเศส). Association Métrodiff. 7 April 1795. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 17 August 2016. สืบค้นเมื่อ 8 December 2012.
Litre, la mesure de capacité, tant pour les liquides que pour les matières sèches, dont la contenance sera celle du cube de la dixièrne partie du mètre.
English translation: ‘Litre: unit of capacity for both liquids and solids which will be equivalent to a cube of [with sides] one tenth of a metre.' - ↑ "NIST, 2000". Ts.nist.gov. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 10 December 2011. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2012-04-26.
บรรณานุกรม
แก้- Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (2006). "The International System of Units (SI)" (PDF). สืบค้นเมื่อ 2008-08-18.
- Bureau International des Poids et Mesures. (2006). "The International System of Units (SI)" (on-line browser):
- Table 6 (Non-SI units accepted for use with the International System). Retrieved 2008-08-24
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (11 November 2000). "Appendix C: General tables of units of measurement". NIST Handbook 44: Specifications, Tolerances, and Other Technical Requirements for Weighing and Measuring Devices. National Institute of Standards and Technology. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 10 December 2011. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2006-10-09.
- National Institute of Standards and Technology. (December 2003). The NIST Reference on Constants, Units, and Uncertainty: International System of Units (SI) (web site):
- Note on SI units. Retrieved 2008-08-24.
- Recommending uppercase letter L. Retrieved 2008-08-24.
- Taylor, B.N. and Thompson, A. (Eds.). (2008a). The International System of Units (SI) เก็บถาวร 2016-06-03 ที่ เวย์แบ็กแมชชีน. United States version of the English text of the eighth edition (2006) of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures publication Le Système International d' Unités (SI) (Special Publication 330). Gaithersburg, MD: National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved 2008-08-18.
- Taylor, B.N. and Thompson, A. (2008b). Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (Special Publication 811). Gaithersburg, MD: National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved 2008-08-23.
- Turner, J. (Deputy Director of the National Institute of Standards and Technology). (16 May 2008)."Interpretation of the International System of Units (the Metric System of Measurement) for the United States". Federal Register Vol. 73, No. 96, p. 28432-3.
- UK National Physical Laboratory. Non-SI Units